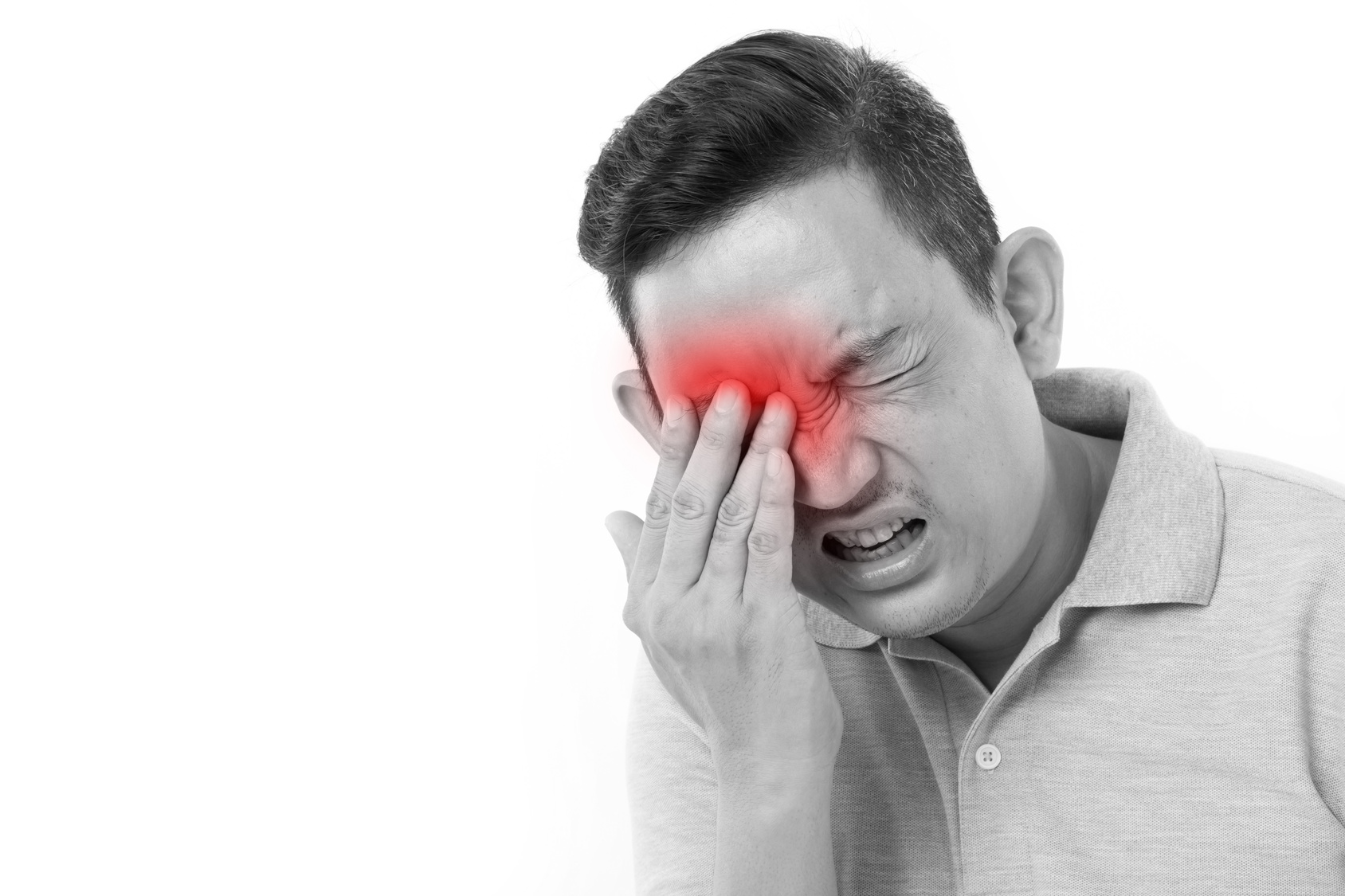


When this is blocked, pressure builds up quickly, and immediate medical attention is needed to protect the vision. However, this type of glaucoma is painless.Īngle-closure glaucoma occurs when a person’s iris blocks the drainage angle where eye fluid leaves the eye. Primary open-angle glaucoma is where eye fluid does not drain correctly, causing damage to the optic nerve. Risk factors include a family history of the condition and other eye-related injuries or surgeries. The two types of glaucoma are primary open-angle and angle-closure. In cases where the blood clot is septic and potentially fatal, a person may require hospitalization, often in an intensive care unit. Doctors do not recommend surgical interventions for the cavernous sinuses themselves. However, there is also some controversy surrounding anticoagulants as they can result in hemorrhage or bleeding.Īnother option that doctors often prescribe is corticosteroids, as there is a potential benefit of reducing inflammation. Doctors typically prescribe these for several weeks to several months.ĭoctors consider this type of treatment effective in slowing down the progression of blood cots and reducing the mortality rate. Other experts recommend anticoagulants to thin blood and therefore prevent further blood clots. They should monitor patients’ conditions closely even after the discontinuation of antibiotics. Other symptomsĭoctors tend to treat this condition with antibiotics and antimicrobial therapies, typically for 3–4 weeks. People with uncontrolled diabetes or receiving treatment for cancer may be at risk of developing cavernous sinus thrombosis. Septic cavernous sinus thrombosis can occur due to the following conditions: A bacterial infection often causes this condition. The cavernous sinus is a vein running between the bottom of the brain to the back of the eye sockets. This rare condition occurs when a potentially life threatening or a septic blood clot develops in the cavernous sinus. certain medications, including sleeping pills or hormonal treatments.environmental factors, including smells, temperatures, sounds, or lights.
hormonal imbalances, for example, during pregnancy or menstruation.food additives and artificial sweeteners.certain foods, like aged cheeses and red wine.The best remedy to prevent migraine is to avoid triggers where possible. If migraine attacks are severe or happen frequently, a doctor may recommend taking daily medication like beta-blockers. These medications balance the chemical changes leading to a migraine and include: However, people with migraine often need prescription medications. Treatmentĭoctors may recommend nonprescription medications, such as aspirin and ibuprofen. Migraine headaches may also cause people to feel nauseated or experience vomiting. These disturbances may occur on only one side of the head and worsen with movement, exposure to sound, light, or strong smells. Migraine symptoms may also include visual disturbances, such as: Migraine affects roughly 2 in 10 people, occurs in females more than males, and tends to run families. Styes: How you can avoid them and best treatment tips.Migraine is a common condition related to the brain that can often cause headaches along with extreme pain behind the eye. Efficacy of topical analgesics in pain control for corneal abrasions: A systematic review. Cluster headache: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical features, and diagnosis. Epidemiology of primary ophthalmic inpatient admissions in the United States. Diagnosis and treatment of anterior uveitis: Optometric management. Harthan JS, Opitz DL, Fromstein SR, Morettin CE. The diagnosis and treatment of optic neuritis. Scleritis: Differentiating infectious from non-infectious entities.

Murthy SI, Sabhapandit S, Balamurugan S, et al.
Pain behind eyeballs update#
Update on the management of infectious keratitis. "Narrow angles" a tip-off to eyesight risk.Īustin A, Lietman T, Rose-Nussbaumer J. Diagnosis and management of blepharitis: An optometrist's perspective. Conjunctivitis: A systematic review of diagnosis and treatment. What can photophobia tell us about dry eye? Expert Rev Ophthalmol. Galor A, Levitt RC, Felix ER, Sarantopoulos CD. Non-surgical interventions for acute internal hordeolum.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
